
Medical Surgeries
Mastectomy

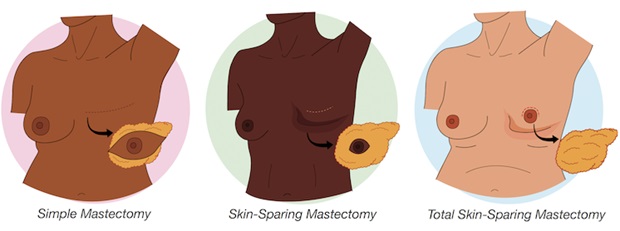
A mastectomy is a surgical procedure in which one or both breasts are removed, typically as a treatment for breast cancer or as a preventive measure in cases of a high risk of breast cancer. There are several types of mastectomy, including:
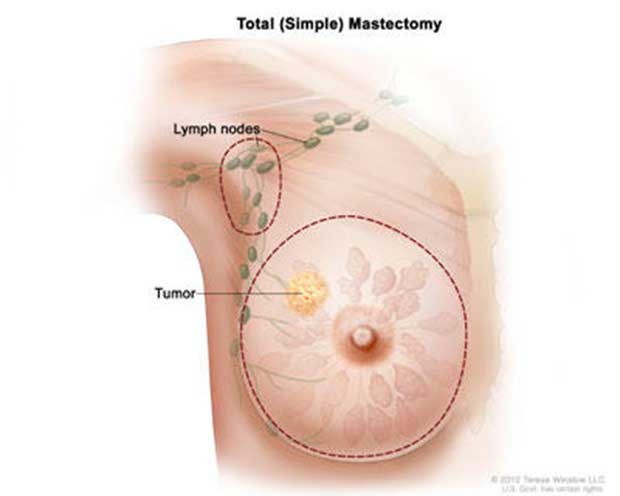
Total or simple mastectomy: In this procedure, the entire breast tissue, including the breast gland, nipple, and areola, is removed, but the chest muscles beneath the breast are preserved.
Modified radical mastectomy: This type of mastectomy involves removing the breast tissue, nipple, areola, and some of the underarm lymph nodes. It is often performed when cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
Radical mastectomy: This procedure is less common today and involves removing the entire breast, underlying chest muscles, and lymph nodes in the armpit. It is typically reserved for very advanced cases of breast cancer.
Double mastectomy (bilateral mastectomy): This is when both breasts are removed. It can be done for various reasons, including the treatment of breast cancer in both breasts or as a preventive measure in cases of a high risk of developing breast cancer.
Mastectomies can have a significant impact on a person's physical appearance and emotional well-being. Some individuals may choose to undergo breast reconstruction surgery to rebuild the shape and appearance of the breast after a mastectomy. Others may opt for prosthetic breast forms or choose not to undergo reconstruction.
Before Mastectomy:
Consultation and Planning: Meet with your surgeon and medical team to discuss the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes. Discuss the type of mastectomy (simple, skin-sparing, nipple-sparing) and whether you'll have breast reconstruction at the same time.
Preparing for Surgery: Follow any preoperative instructions provided by your surgeon, which may include fasting, medication adjustments, and showering with a special antibacterial soap. Arrange for someone to drive you home after the surgery and provide assistance during the initial recovery period.
Emotional Support: Seek emotional support from friends, family, support groups, or a mental health professional to help cope with the emotional aspects of the surgery.
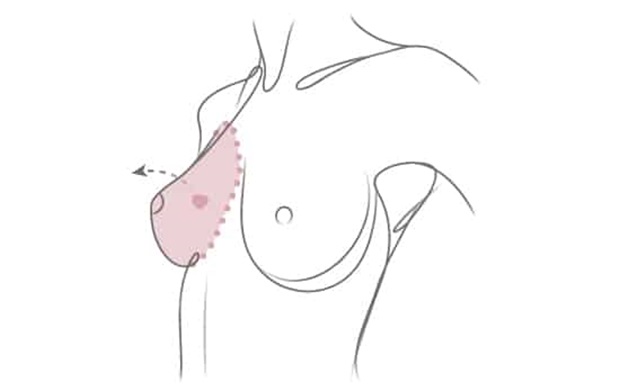


After Mastectomy:
Surgical Site Care: Keep the incision site clean and dry as directed by your surgeon. You may have drains in place to remove excess fluid from the surgical site. Learn how to care for and empty these drains.
Pain Management: You'll likely experience pain and discomfort. Follow your doctor's recommendations for pain management, which may include prescription or over-the-counter pain medications.
Mobility and Exercise: Gradually resume light activities, as recommended by your surgeon. Gentle arm exercises can help prevent stiffness and promote healing.
Lymphedema Prevention: After a mastectomy, there is a risk of developing lymphedema (swelling in the arm). Follow your doctor's guidance on preventing and managing lymphedema.
Dressings and Garments: Wear surgical dressings and compression garments, if prescribed by your surgeon, to support the healing process.
Emotional and Psychological Support: Continue seeking emotional support and consider therapy or counseling if needed. Attend support groups for individuals who have undergone mastectomies to connect with others who have similar experiences.
Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all post-operative follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery and address any concerns.
Scar Management: Discuss scar management with your surgeon, which may include options like silicone gels or sheets to improve the appearance of the surgical scar.
Breast Reconstruction (if applicable): If you plan to have breast reconstruction, discuss the timeline and options with your surgeon.
What are the symptoms of breast cancer?
Breast cancer symptoms can vary, and some individuals with breast cancer may not experience any symptoms at all. It's important to note that having one or more of these symptoms does not necessarily mean you have breast cancer, as many of these signs can also be caused by non-cancerous conditions. However, if you notice any changes in your breasts, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation.
Common symptoms of breast cancer include:
Lump or Mass: The most common symptom is the presence of a lump or thickening in the breast or underarm. This lump may feel different from the surrounding tissue.


Changes in Breast Size or Shape: Breast cancer can cause changes in the size, shape, or appearance of the breast. This may include asymmetry between the two breasts.
Changes in the Skin: Skin changes on the breast, such as redness, dimpling, or puckering, may be indicative of breast cancer.
Nipple Changes: Changes in the nipple, such as inversion (turning inward), discharge (other than breast milk), or changes in the skin around the nipple, can be signs of breast cancer.
Pain: While breast cancer is not always painful, some individuals may experience breast or nipple pain.
Swelling: Swelling or thickening of part of the breast is another possible symptom.

WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF BREAST CANCER?
Breast cancer is a complex disease, and its development is influenced by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. While the exact cause of breast cancer is not fully understood, several risk factors have been identified. It's important to note that having one or more risk factors does not guarantee that an individual will develop breast cancer, and many people with breast cancer have no known risk factors. Here are some factors that may increase the risk of developing breast cancer:
Gender and Age: Women are at a higher risk of developing breast cancer compared to men. Additionally, the risk increases with age, with most cases occurring in women aged 50 and older.
Genetics: Inherited gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can significantly increase the risk of breast cancer. However, most cases of breast cancer are not directly linked to family history.
Family History: Having a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, or child) who has had breast cancer may increase the risk, especially if the relative was diagnosed at a young age.
Personal History: Women who have had breast cancer in one breast have an increased risk of developing cancer in the other breast.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy after menopause may slightly increase the risk of developing breast cancer.
Reproductive and Menstrual History: Early onset of menstruation (before age 12), late onset of menopause (after age 55), and having the first full-term pregnancy after the age of 30 can be associated with a higher risk of breast cancer.
Radiation Exposure: Previous radiation exposure, especially during adolescence or early adulthood, can increase the risk of breast cancer.
Dense Breast Tissue: Women with dense breast tissue may have a higher risk of developing breast cancer.
Lifestyle Factors: Certain lifestyle choices may contribute to the risk of breast cancer, such as excessive alcohol consumption, lack of physical activity, obesity, and a high-fat diet.
Environmental Factors: While research in this area is ongoing, some studies suggest that exposure to certain environmental factors, such as certain chemicals and pollutants, may play a role in the development of breast cancer.
Mastectomy aftercare:
After undergoing a mastectomy, it's crucial to follow a comprehensive aftercare plan to ensure proper healing and overall well-being. Keep in mind that individual experiences may vary, so it's essential to consult with your healthcare team for personalized advice. Here is a general guide to mastectomy aftercare

Wound Care:
- Follow your surgeon's instructions: Your surgeon will provide specific guidelines for caring for the incision site. Follow these instructions carefully.
- Keep the incision clean and dry: Clean the incision site as directed by your healthcare provider. Avoid soaking in baths until approved by your surgeon.
- Monitor for signs of infection: Watch for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, increased pain, or discharge. Contact your healthcare team if you notice any concerning symptoms.
Pain Management:
- Take prescribed medications: Use pain medications as prescribed by your doctor to manage post-operative pain. Inform your healthcare provider if you experience any side effects or if the pain is not well controlled.
Physical Activity:
- Gradual return to activity: Follow your healthcare provider's guidance on when it's safe to resume normal activities and gradually increase your level of physical activity.
- Avoid heavy lifting: Refrain from lifting heavy objects or engaging in strenuous activities until approved by your surgeon.
Lymphedema Prevention:
- Range of motion exercises: Perform gentle arm exercises as recommended by your healthcare team to maintain flexibility and prevent lymphedema.
- Compression garments: If prescribed, wear compression garments to reduce the risk of lymphedema.
Emotional Support:
- Counseling and support groups: Consider joining a support group or seeking counseling to help cope with the emotional aspects of mastectomy and body image changes.
Follow-Up Appointments:
- Regular check-ups: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon and oncologist.
- Monitoring for recurrence: Be vigilant about any changes in your body and report them promptly to your healthcare team.
Scar Care:
- Scar massage: If advised by your surgeon, gently massage the scar tissue to promote healing and reduce tightness.
- Sun protection: Protect the incision site from the sun to minimize scarring.
Nutrition and Hydration:
- Healthy diet: Maintain a well-balanced diet to support overall healing and recovery.
- Adequate hydration: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, which is crucial for recovery.
Breast Reconstruction (if applicable):
- Discuss reconstruction options: If you're considering breast reconstruction, talk to your surgeon about the available options and timing.
Always communicate openly with your healthcare team about any concerns or questions you may have during your recovery. They can provide valuable guidance and support based on your circumstances.


Our services include:
![]() our online services include: quotes and consultation
our online services include: quotes and consultation
![]() Planning the highest word-level medical trips and quality hospitals and medical centers according to the patient's request and budget.
Planning the highest word-level medical trips and quality hospitals and medical centers according to the patient's request and budget.
![]() Appointing treatments by the most skilled and experienced doctors.
Appointing treatments by the most skilled and experienced doctors.
![]() Airport pick-up/drop off, check-ups, accompanying translator, book hotel (for patients and their families)
Airport pick-up/drop off, check-ups, accompanying translator, book hotel (for patients and their families)
![]() Pre-hospitalization / post-hospitalization care services
Pre-hospitalization / post-hospitalization care services
All-Inclusive Medical Travel Packages
based on your budget, our team will assist you in choosing the best hotels, doctors, and medical centers. Our packages include:
 Airport Pickup Services
Airport Pickup Services Airport Dropoff services
Airport Dropoff services Hotel
Hotel Ticket
Ticket visa
visa translator
translator Transfer
Transfer SIM Card
SIM Card Sightseeing
Sightseeing


 why Iran
why Iran
Patients may choose to have abdominoplasty (commonly known as a tummy tuck) in Iran for a variety of reasons
Cost, Quality of Care, Privacy and Discretion, Combined Tourism, no Waiting Times
![]()
Fotros is an Iranian health tourism company with a professional team consisting of a support team and word-level doctors in medical and cosmetic surgeries like Neurosurgery, Rhinoplasty, Breast cosmetic surgeries, Liposuction, tummy tuck, etc.









 why Iran
why Iran